With stricter requirements for payment security and compliance with standards such as AML, KYC, and PSD2/PSD3, a secure payment system must do more than just protect transactions. It also needs to monitor activity, track transactions, and respond quickly to unusual behavior.
As online payments continue to grow and fraud becomes more sophisticated, payment systems are being strengthened with modern fraud detection technologies. These technologies help keep transactions safe and reduce financial losses caused by payment fraud.
Online Transaction Fraud Detection Mechanism
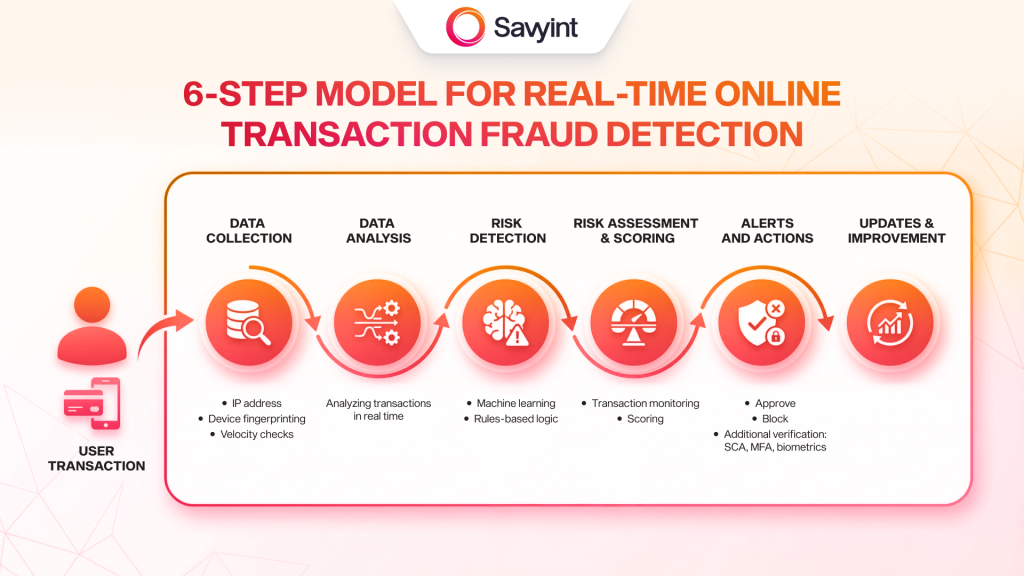
Modern online fraud detection models are designed to spot unusual behavior early, so risks can be stopped during the transaction instead of being handled only after fraud has already happened. In general, fraud detection systems follow a process with six main steps:
- Step 1: Data Collection
- Step 2: Data Analysis
- Step 3: Risk Detection
- Step 4: Risk Assessment and Scoring
- Step 5: Alerts and Actions
- Step 6: Continuous Updates and Improvement
Step 1: Data Collection
Data collection is the foundation of any fraud detection system. To accurately assess the risk of a transaction, the system needs to collect different types of data related to users, devices, and transaction behavior.
- IP addresses provide basic information about a user’s internet location. Unusual IP changes, especially from high-risk regions, can be a warning sign of fraud.
- Device fingerprinting collects identifying details such as operating system, screen size, and browser version from computers, mobile phones, and tablets in real time. This information is used to build device profiles that help detect fraud risks, identify users, personalize user experiences, and protect systems from cyber threats.
- Velocity checks monitor how often transactions are made from the same IP address or account within a certain period of time. If the activity looks abnormal, the system may flag it for further review or reject the transaction.
Step 2: Data Analysis
Data analysis plays a key role in preventing online payment fraud. In the past, many organizations only reviewed transactions after they were completed, when fraud had already occurred. In most cases, recovering money from fraudulent transactions is very difficult or even impossible.
That is why businesses now focus on detecting and stopping fraud before a transaction is completed. By analyzing transactions in real time, monitoring user behavior, and tracking the full customer journey – from login to payment – the system can quickly identify and block fraud risks.
Step 3: Risk Detection
Based on the collected and analyzed data, the system detects risks using machine learning or rules-based logic. Machine learning allows the system to learn from large amounts of data, recognize normal and abnormal behavior patterns, and predict fraudulent transactions more accurately in real time.
Alongside machine learning, predefined rules also help detect suspicious transactions. For example, transaction limits can be set so that transfers above a certain amount – such as USD 1,000 – are blocked or require additional verification.
Step 4: Risk Assessment and Risk Scoring
Using identified risk signals, the system evaluates each transaction and assigns a risk score. Based on this score, transactions are classified as either “legitimate” or “suspicious.”
Step 5: Alerts and Actions
If a transaction is marked as suspicious, the system sends an alert to the security team so immediate action can be taken. This may include blocking the transaction, asking for additional verifications such as Strong Customer Authentication (SCA), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), biometric verification, or contacting the customer for further confirmation.
Step 6: Continuous Updates and Improvement
Fraud detection models are continuously updated and improved using new data and past fraud cases. This helps increase accuracy and allows the system to adapt to new and more advanced fraud techniques.
Comprehensive Fraud Prevention with Savyint Fraud Prevention & Risk Management
Built around the six- step fraud detection and prevention model, Savyint Fraud Prevention & Risk Management (FPRM) helps banks and financial institutions detect, prevent, and respond effectively to fraud. This reduces losses, strengthens transaction security, protects customer data, and improves long-term operational efficiency.
With a Zero Trust architecture, Savyint FPRM enables:
- Comprehensive data collection
- Data analysis through end-to-end real-time transaction monitoring, AI/ML-based behavior analysis, integration of advanced device intelligence for device identification, micro-behavior analysis, and anonymous fraud detection
- Real-time risk assessment and risk scoring
- Advanced user authentication using AI combined with Strong Customer Authentication (SCA), multi-layer Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), biometric authentication, and 3D Secure
- Enhanced transaction security through tokenization and post-quantum cryptography (Post-Quantum Cryptography – PQC), meeting future security requirements
Savyint Fraud Prevention & Risk Management (FPRM) complies with global standards such as AML, KYC, KYB, PSD2, PSD3, and PCI-DSS, as well as local regulations including Circulars 64 and 50 (Vietnam), BSP 1213 (Philippines), and regulations in Malaysia.
Contact Savyint experts today to strengthen security and implement effective payment fraud prevention strategies.
Source: How payment fraud works – Tipalti







