
RootCA Trust with certification authorities compliance Webtrust
Root certification authorities (CAs) are deployed as trust anchors in public key infrastructure (PKI) solutions used to issue digital certificates in an organization. Root CAs in a simple PKI hierarchy certify sub-ordinate CAs (often referred to as Issuing CAs) which then issue digital certificates to “end entities” such as Web servers, workstations or individuals. These entities use digital certificates, and the public/private keys associated with them, to identify themselves on the network or perform other functions such as encrypt and/or sign information or messages.
The physical separation of trust anchor (rootCA) and Issuing CAs in the PKI hierarchy is designed to minimize the risk of compromise of the rootCA and therefore of the entire PKI. As part of the risk mitigation of the root CA it is protected using both physical and logical controls.
There are several components involved in PKI, combining services and technologies. All those roles can be performed by the same organization, but some of them may be outsourced (with limitations)
PKI System Solution
1. PKI Server Solution
PKI Servers are responsible for managing the complete life cycle of setting up Certification Authorities. It starts by setting up a Root CA followed by Subordinate CAs issuing, validating, and revoking end-entity (users, devices, IOT) X.509 digital certificates & CRLs. This allows all communication and transactions between users and devices to be secure, trusted, and authenticated. By providing a secure and trusted infrastructure for managing digital certificates and keys, PKI Server enables organizations to establish a strong foundation of trust in their networked environments. This helps to protect sensitive information, prevent data breaches, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. With blazing fast speed, great user experience, multilingual UI and complying with all security standards PKI Server simplifies your day-to-day PKI administration.
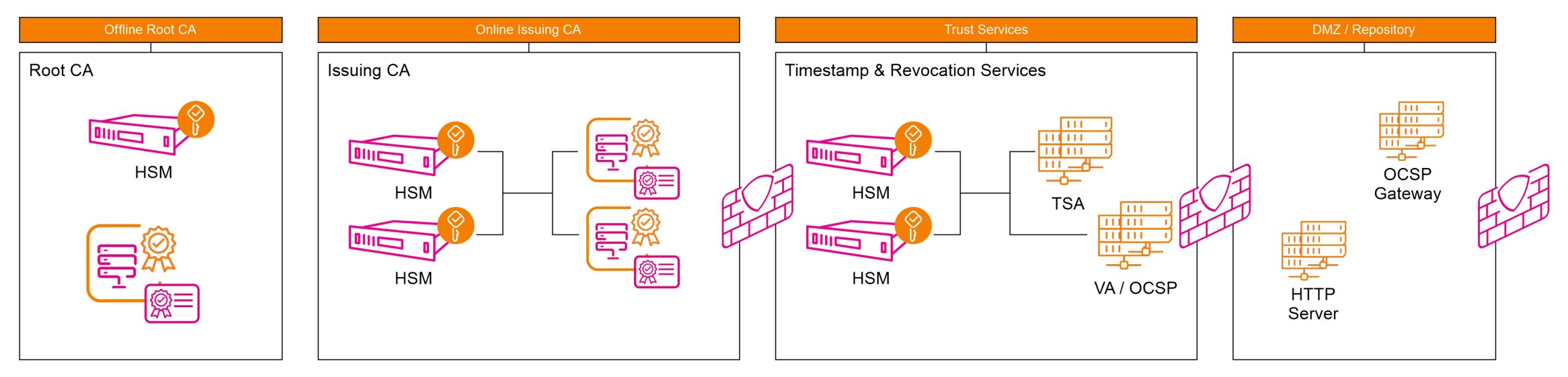
Overview of the System Model
PKI server system includes the following components:
RootCA
(Root Certification Authority)
This is the server responsible for issuing digital certificates and owning the root certificate. The primary function of RootCA is to provide services for issuing and verifying certificates for IssuingCAs
IssuingCA
(Issuing Certification Authority)
This is the server that issues certificates and owns the issuing certificate. The main function of IssuingCA is to provide services for issuing and verifying certificates for public CAs
HSM (Hardware Security Module) for RootCA
A mandatory component used to secure the cryptographic keys of the RootCA server. The HSM enables RootCA to perform cryptographic functions, including encryption and certificate issuance. It complies with technical standards required for digital signatures
LDAP/Database
A server responsible for managing and storing information related to digital certificates
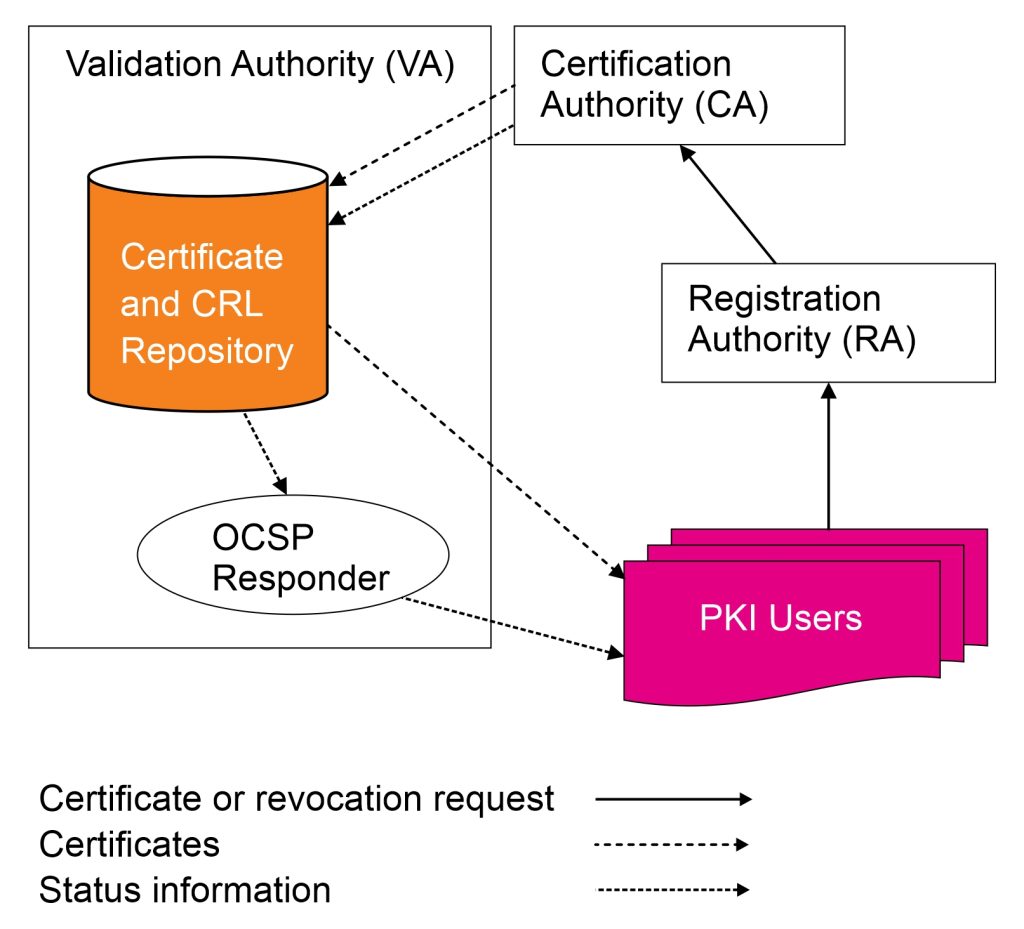
VA System
(Validation Authority)
Comprising OCSP (Online Certificate Status Protocol) and CRL (Certificate Revocation List), this system is used to verify the authenticity and status of certificates (valid or revoked)
TSA System
(Timestamp Authority)
Comprising OCSP (Online Certificate Status Protocol) and CRL (Certificate Revocation List), this system is used to verify the authenticity and status of certificates (valid or revoked)
SAVYINT PKI IN A BOX
Savyint PKI in a Box is an all-in-one PKI appliance designed to meet the needs of organizations of all sizes. With the ability to issue and manage digital certificates for up to hundreds of millions of users, this solution is ideal for enterprises, government agencies, and critical service providers. Savyint PKI in a Box provides solutions with the following configurations.

2. Timestamp Authority (TSA)
Proving time is important in high valued transactions and critical for businesses creating digital signatures for long-term perseverance. Without cryptographic timestamps, digital signatures can’t be trusted as they cannot be accepted in the long term. Timestamp servers provide proof of data existence at a particular point in time using cryptography. With the emergence of elDAS regulation, allowing cross border digital signature acceptability, TSAs have now become a corner stone in the evolving digital trust landscape.
- Fully meets all functionalities.
- Supports creation of advanced digital signatures based on IETF and ETSI standards including XAdES-T, CAdES-T, PAdES-T supporting ETSI EN 319 421; ETSI EN 319 422 and RFC 3161. Works seamlessly with wide range of business apps to integrate timestamping i.e. Adobe Acrobat, Microsoft Office, SignTool etc
- Timestamp server can be configured to use system time either already synched with a trusted time source or NTP. Administrators can directly configure multiple NTP sources based on stratum to avoid a single point of failure
- Keeping in view businesses having differen cryptographic needs, signing serve supports diverse cryptographic
- Requirements such as: RSA (2048, 4096, 8192), ECDSA (192, 224, 256, 320, 384, 512), SHA-256, 384 and 512
- Software support database inculde (Postgres, Oracle, MySQL)
- Timestamp Server records all incoming transactions for detailed analysis with unique identifiers (marked by CPU serial no + unique no). Administrator can also download and investigate request/responses on the fly
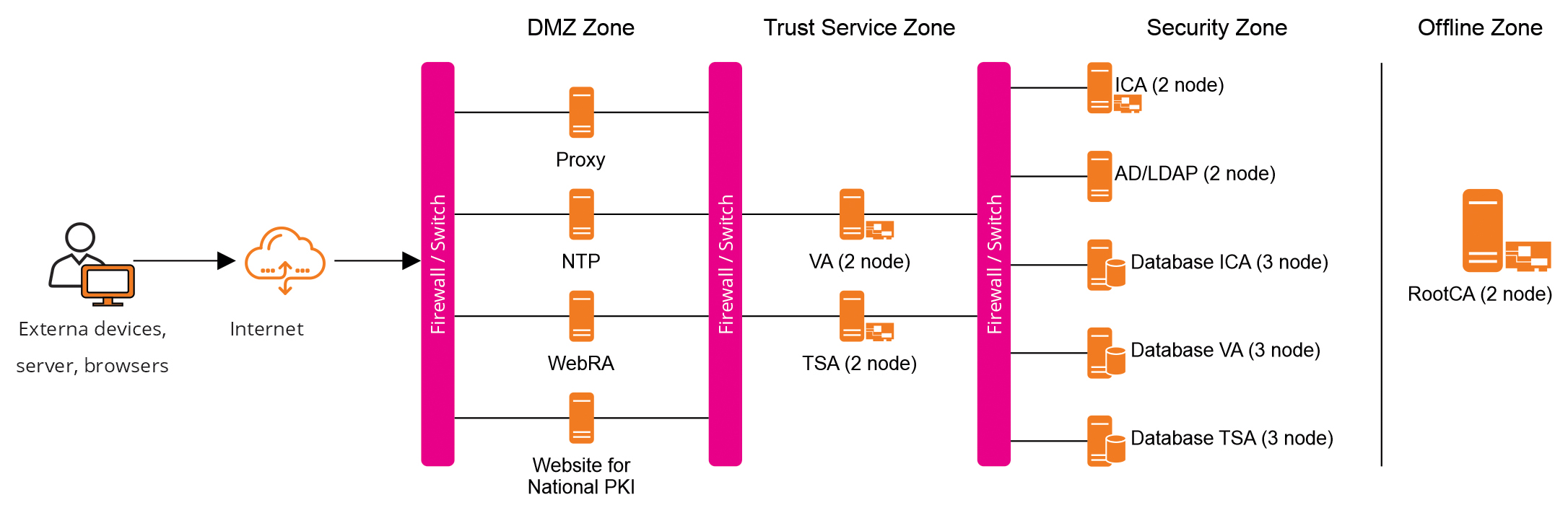
Overview of the System Model of Time Stamping Authority
