Open banking is a new financial ecosystem that allows users to securely share their personal financial data with third-party organizations, which can be fintech companies or other financial institutions. By sharing data, these organizations can provide personalized financial services to users. So how is open banking data being processed and what is it used for?
Open banking: Managing user consent for data access (consent management)
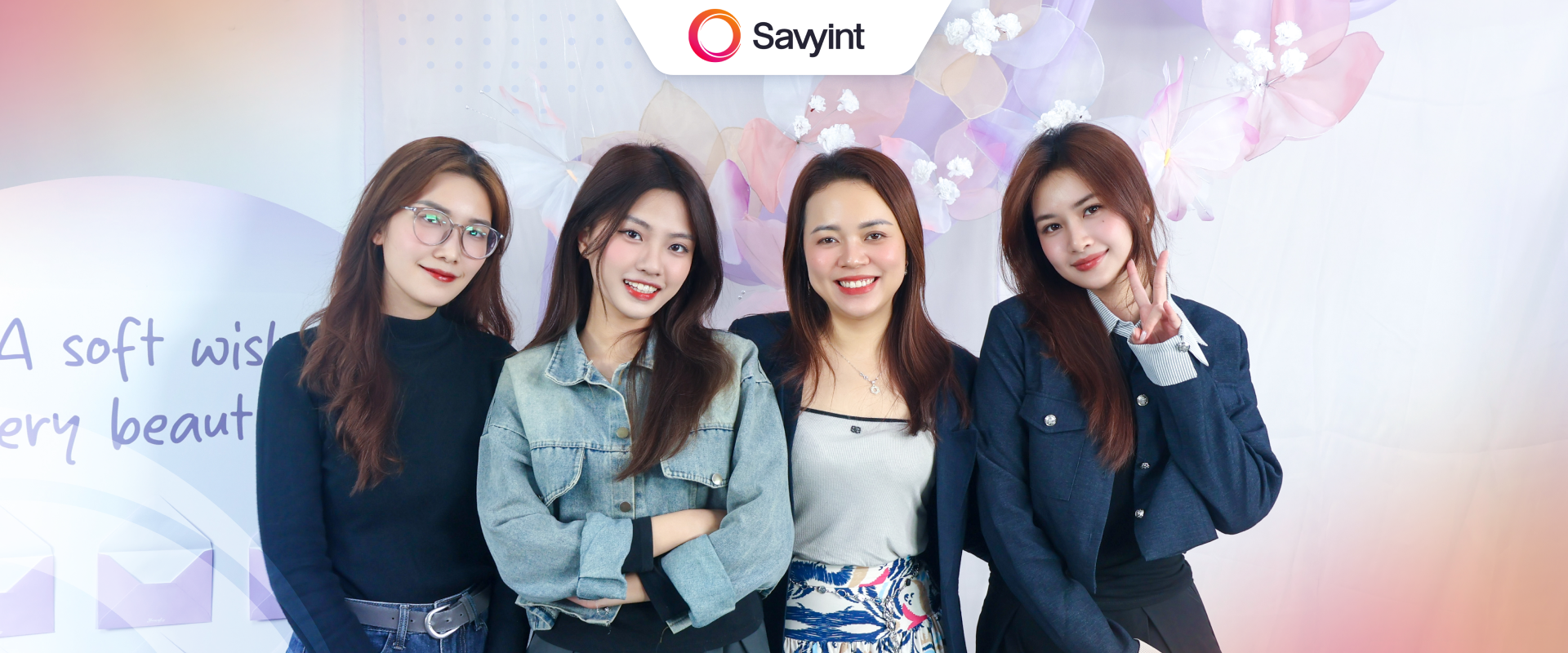
To provide and develop quality products and services, third-party providers (TPPs) need user consent to access their financial data, which is then filtered and processed for research purposes, and to build new financial products and services.
Consent management is a sensitive issue that requires caution and understanding of legal and technical aspects. Contrary to popular belief, consent management is not simply clicking or checking the “Agree” box; it is a structured process that complies with regulations and directives in each region and country, such as the PSD2 directive or GDPR regulations in the EU.
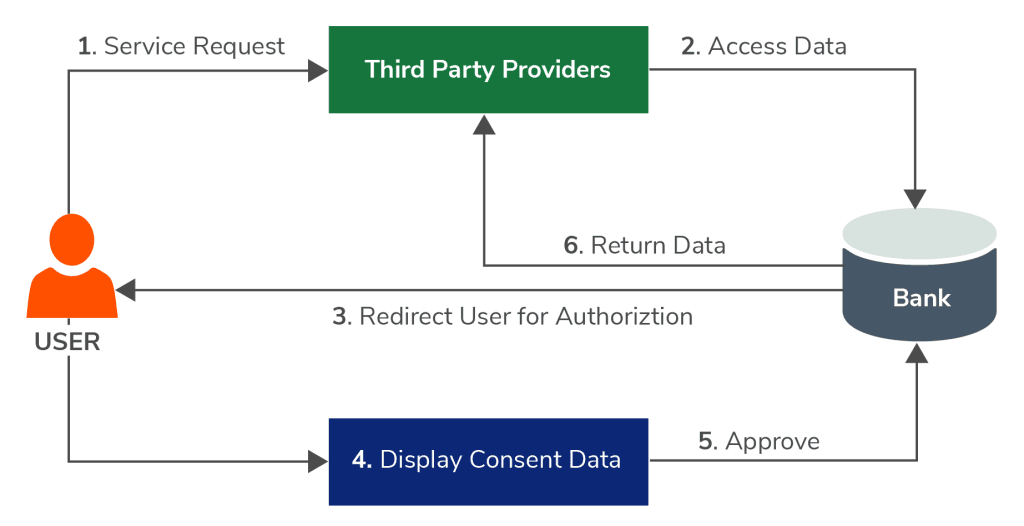
The approval management process in banking usually proceeds as follows:
- Third-party providers notify about the purpose and the data to be collected, requiring consent from the customer
- The customer agrees by confirming
- Then, the data will be transferred from the Account Information Service Provider (AISP) to the third-party provider or from the Payment Initiation Service Provider (PISP) to the bank
Some organizations may have different ways of expressing the agreement to access data, but this will be the most common mechanism, often used in:
- Mobile authentication
- Logging into the bank account
- Digital signature
Understanding how data and information flow during the consent request process is a key factor in the transparency and success of organizations in open banking.
The process of managing the approval of open banking data sharing
The approval management process is typically divided into three stages:
a. Agreement stage
- Users receive notifications about the purpose and the data being used; users will choose to approve or decline this content.
- If approved, users will be informed about the duration of data access authorization to ensure they always control their data;
b. Verification stage
- The bank receives the information and requires users to perform verification to ensure data security;
- The identity of the user is verified. At this step, the third-party provider will not see the user’s authentication information.
c. Authorization stage
- The bank notifies users about the data that will be shared with third-party providers; and allows users to decline this notification;
- User feedback is sent back to the bank
Throughout the process, users are always aware of who they are granting data access to, for how long, and for what purpose. In particular, users can withdraw consent at any time. The information users are aware of typically includes:
- Who is accessing their data: The name of the third-party provider;
- For how long: Duration
- For what purpose: Account/payment details
- Expiration process: when it will expire and how users can withdraw consent?
Open banking data sharing: How does it work?
Open banking allows third-party financial service providers to access information with the user’s permission. Technically, this process is carried out through open APIs. Legally, the data sharing process is monitored and regulated according to current government regulations, such as the Payment Services Directive PSD2 in the EU or the Open Banking Act in the UK.
However, these regulations vary by region, so the types of data shared through open banking services also differ. Typically, to ensure transparency and integrity, there will be multiple layers of security and verification in the data exchange process between financial institutions and third-party providers. The transmission of data from one side to the other is done in “an instant” thanks to APIs to ensure seamless, safe, and efficient communication.
Who can access open banking data?
Not everyone can access data in open banking. To view this data, consent from the user is required, and the third-party provider must also be licensed. Third-party providers must meet specific requirements before being granted access to the user’s financial information.
Regulatory authorities will be responsible for granting access to user data for third-party providers, such as in Australia, where the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) is responsible for licensing open banking data.
These authorities are responsible for ensuring that the sharing of personal financial data does not violate the law and can grant, modify, or revoke data collection licenses.
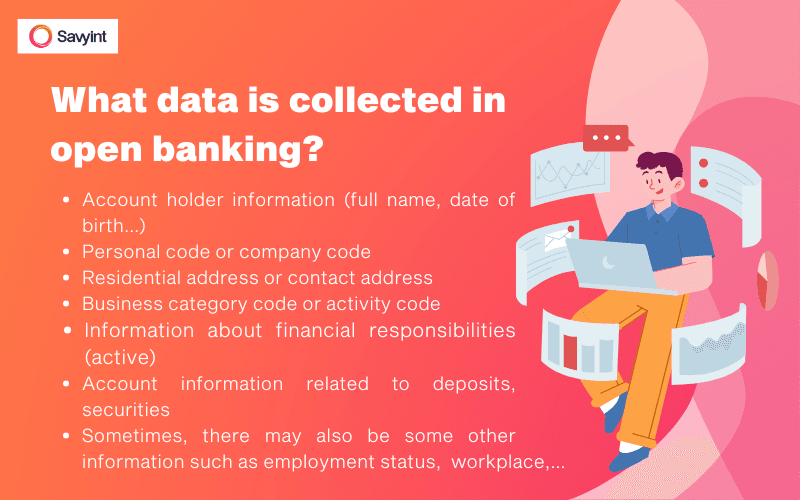
What data is collected in open banking?
The data collected by open banking service providers may vary depending on the regulations of each country/region as well as the type of services provided.
Regulatory authorities often impose strict regulations on the type of information that can be collected, limiting the scope of data collection to ensure that third-party providers only access what is necessary. The most commonly collected data includes:
- Account holder information (full name, date of birth…)
- Personal code or company code
- Residential address or contact address
- Business category code or activity code
- Information about financial responsibilities (active)
- Account information related to deposits, securities
- Sometimes, there may also be some other information such as employment status, workplace,…
How do open banks protect user data?
In fact, data protection in open banking is a matter of great concern to regulatory agencies and financial institutions. Security measures implemented include:
- Strict regulations/laws: Each country or region will have its own regulations and directives to ensure stable operations or data security, such as the PSD2 directive in the EU or the Open Banking Act in the UK,…
- Advanced security technology: Banks and service providers use advanced security technologies such as encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and fraud detection to protect customer data.
- Risk management: Financial institutions regularly assess and manage potential security risks, while also having emergency response plans in case of incidents.
- Transparency: Users are always clearly informed about the type of data shared, the purpose of use, and how data is protected.
- User control rights: Users have the right to control the sharing of their data, including the ability to withdraw consent at any time.
However, alongside protective measures, there are still some risks that developers and users are concerned about, such as:
- Threats from malware: Malware can exploit security vulnerabilities to steal data.
- Data attacks
- Hackers: Hackers are always looking for vulnerabilities to infiltrate systems and steal data.
In summary, while it is impossible to completely eliminate risks, current security measures have been established to ensure that user data is safely protected in open banking systems. However, users should also protect themselves by using strong passwords, regularly updating software, and being vigilant against phishing attacks.
Additionally, allowing users to manage open banking data is also a great way for users to take responsibility for when and how they want to provide their information. Third-party providers need to clearly inform about the purpose and the data that will be collected to ensure transparency and the privacy of open banking data.
About SAVYINT and the SAVYINT Open Banking solution
SAVYINT is a trusted service provider leading the market and is in the TOP 10 leading IT companies in Vietnam. SAVYINT has successfully developed the SAVYINT Open Banking solution – a specialized system dedicated to the Finance – Banking sector, meeting legal and technological requirements to create connections and build a digital financial ecosystem. With a solid technological infrastructure and experience in deployment and operation, SAVYINT provides customers with advanced technology and the best user experience.
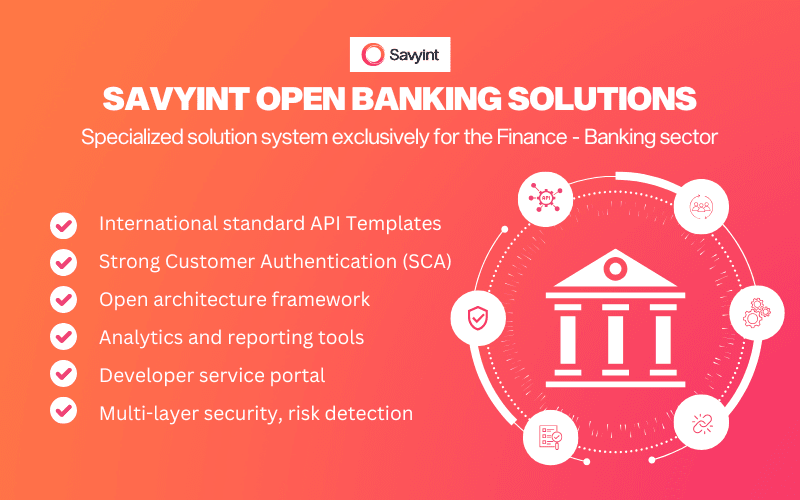
The SAVYINT Open Banking solution encompasses all the features to become a reputable standard platform in the Finance – Technology field:
- International standard API Templates: Supports Open Banking technical standards from leading global organizations such as Berlin Group, UK Group, Monetary Authority of Singapore, Australian Competition and Consumer Commission, Hong Kong Monetary Authority, etc.
- Strong Customer Authentication (SCA): Supports strong authentication in electronic payments and transactions, adaptive authentication, and consent management according to GDPR.
- Open architecture framework: Allows for the flexible development and construction of services based on the Open Banking platform.
- Multi-layer security: Supports multiple layers of API security such as OAuth2, authentication using digital certificates according to eIDAS standards, ensuring absolute safety.
- Analytics and reporting tools: Provides analytics, reporting, and API statistics tools suitable for the operational needs of organizations and businesses.
- Developer service portal: Supports Dev/Test environments, facilitating development and testing.
- Easy and secure Core Banking integration: Ensures quick and absolutely secure integration with existing Core Banking systems.
- Risk detection: Provide risk analysis tools in transactions, detect counterfeit, abnormal, and unsafe characteristics.
Open banking applications are the key to accelerating growth in the financial sector. Connect with SAVYINT now to leverage and experience the features and benefits of open banking today!







